Twisted-Pair
Twisted pair is the ordinary copper wire that connects home and many business computers to the telephone company. To reduce crosstalk or electromagnetic induction between pairs of wires, two insulated
copper wires are twisted around each other. Each connection on twisted pair requires both wires. Since some telephone sets or desktop locations require multiple connections, twisted pair is sometimes installed in two or more pairs, all within a single cable.
Coaxial Cable
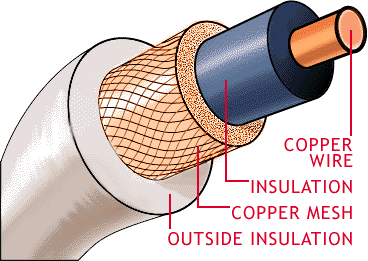 Coaxial cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies between the community antenna and user homes and businesses. Coaxial cable is sometimes used by telephone companies from their central office to the telephone poles near users.
Coaxial cable is the kind of copper cable used by cable TV companies between the community antenna and user homes and businesses. Coaxial cable is sometimes used by telephone companies from their central office to the telephone poles near users.
Fiber-Optic Cable
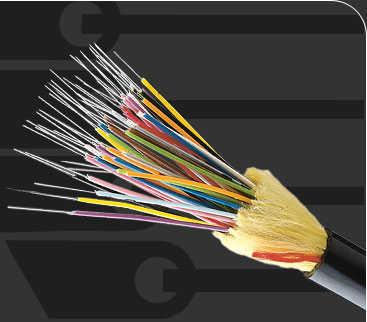
A technology that uses glass (or plastic) threads (fibers) to transmit data. A fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads, each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves.
Network Terms
Node
In a network, a node is a connection point, either a redistribution point or an end point for data transmissions. In general, a node has programmed or engineered capability to recognize and process or forward transmissions to other nodes.
Client
A client is the requesting program or user in a client/ server relationship. For example, the user of a Web browser is effectively making
client requests for pages from servers all over the Web. The browser itself is a client in its
relationship with the computer that is getting and returning the requested HTML file. The computer handling the request and sending back the HTML file is a server.
Server
 In information technology, a server is a computer program that provides services to other computer
In information technology, a server is a computer program that provides services to other computer
programs (and their users) in the same or other computers. The computer
that a server program runs in is also frequently referred to as a server (though it may be used for other purposes as well).
Hub
A common connection point for devices in a network. Hubs are commonly used to connect segments
of a LAN. A hub contains multiple ports. When a packet arrives at one port, it is copied to the other ports so that all segments of the LAN can see all packets.
Network Interface Card ( NIC)
Often abbreviated as NIC, an expansion board you insert into a computer so the computer can be connected to a network. Most NICs are designed for a particular type of network, protocol, and media, although some can serve multiple networks.
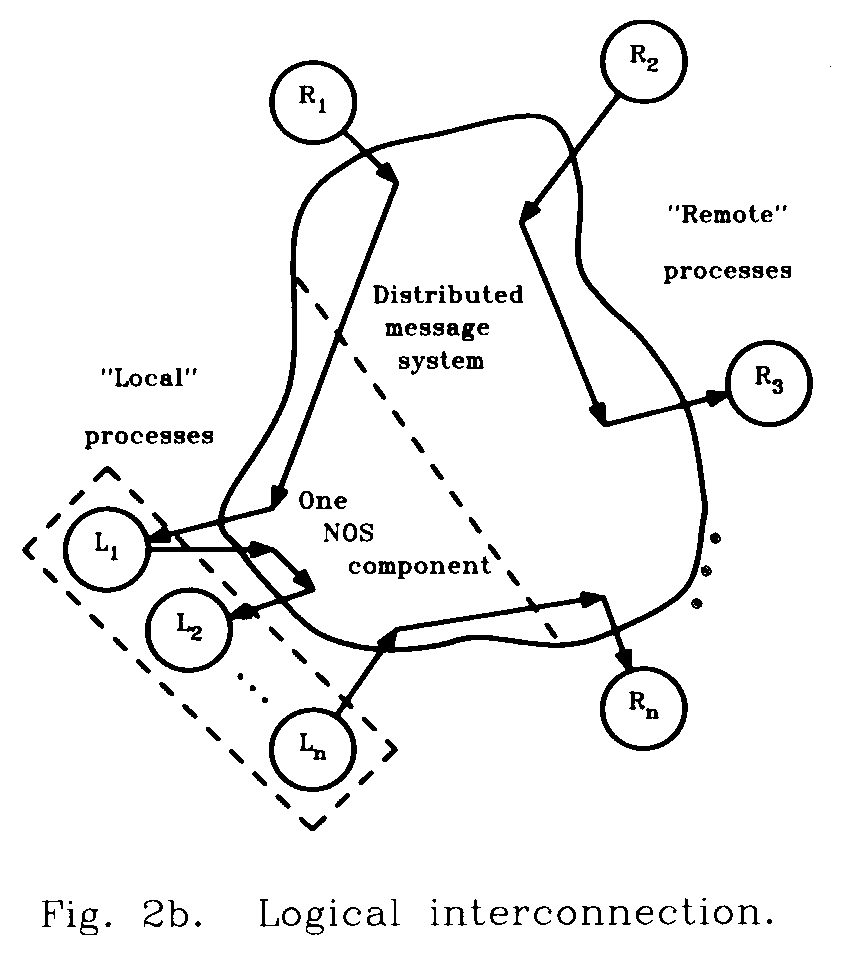
Network Operating System (NOS)
A network operating system (NOS) is a computer operating system system that is designed primarily to support workstation, personal computer, and, in some instances, older terminal that are connected on a local area network (LAN) Artisoft's LANtastic, Banyan VINES, Novell's Netware, and Microsoft's LAN Manager are examples of network operating systems. In addition, some multi-purpose operating systems, such as Windows NT and digital's openVMS come with capabilities that enable them to be described as a network operating system.
Host Computer
In computer networking, a network host, Internet host, host, or Internet node is a computer connected to the Internet - or more generically - to any type of data network. A network host can host information resources as well as application software for providing network services.
Network Manager
NetworkManager is a software utility aimed at simplifying the use of computer network on Linux and other Unix-Like operating systems.The project was initiated in 2004 by Red-Hat, with the goal of enabling Linux users to more easily deal with modern networking needs, particularly wireless networking. NetworkManager takes an opportunistic approach to network selection, attempting to use the best available connection as outages occur, or the user roams between wireless network. Ethernet connections are preferred over “known” wireless networks, which are preferred over wireless networks with SSIDs to which the user has never connected. The user is prompted for WEP or WPA keys as needed.